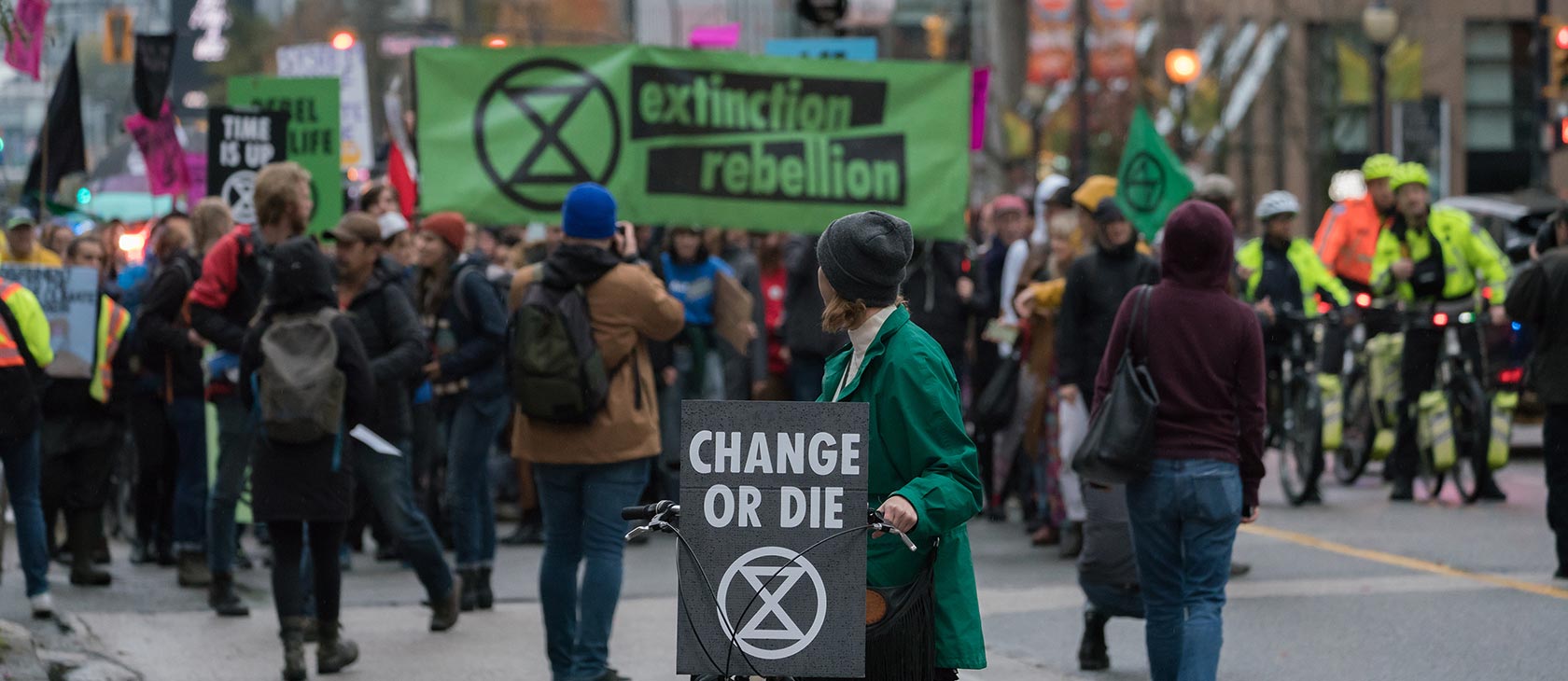We’ve just put online the Fall 2020 issue of Religion & Liberty, which looks at environmental stewardship and current problems in conservation from a number of aspects (get over to Acton’s Facebook page to comment on the articles).
In the cover story, I wrote about the demands for a “citizen’s assembly” to accelerate the agenda of the radical environmental organization Extinction Rebellion. Presumably, these new assemblies won’t involve elected bodies like the U.S. Congress or the Parliament of the United Kingdom:
… perhaps nowhere are the adolescent fantasies of environmental apocalypse – and the sort of high-certitude, simplistic responses to life’s problems commonly heard from teenagers – more pronounced than in the Extinction Rebellion phenomenon. It aims for a net-zero emissions economy by 2025, five years ahead of Ocasio-Cortez’s plan. “XR” is known for disrupting or shutting down roads and public transport in major cities worldwide. Never mind that the great mass of humanity is trying to get to work, pay their bills, take care of their families, and “keep the fairytales of eternal economic growth” chugging along.
XR wants “governments to accede to a key demand: creating a citizen’s assembly that accelerates society away from climate-destroying industries.” It aims for a “tipping point” of 3.5 percent of the population mobilized and eager to sweep away the slow-moving deliberations of democracies that obstruct our net-zero future. “We do not trust our government to make the bold, swift, and long-term changes necessary to achieve these changes, and we do not intend to hand further power to our politicians, ” XR announces.
XR isn’t saying when its citizen’s assembly will hand back the levers of power to democratically elected governments. Its political theorists cite the toppling of repressive regimes – Milosevic in Serbia and Marcos in the Philippines – as evidence that a highly committed cadre can effect change. The group might also have cited the relatively small numbers of Bolsheviks and Mensheviks in Russia in 1910 (fewer than 100,000 in a nation of some 125 million).
Then there’s Greta Thunberg, the 17-year-old Swedish activist who has been scolding leaders of industrialized nations about the need to de-carbonize their economies. She’s the perfect cat’s-paw for environmental activists on the left who have been busily organizing children’s crusades on climate change to shame the grown ups. But here’s a puzzle: Would you allow an angry, know-it-all teenager to run your household? Then why would you listen to her industrial policy?
Religious cultures have often had deep strains of apocalyptic or millenarian sentiment, including the Christian and Jewish traditions, but the extreme forms of environmental apocalyptic today are rooted in the material and and are devoid of any sort of (excuse me here for the $5 word) eschatological aim such as the renewal of Creation or deriving some meaning out of final things. No, movements like Extinction Rebellion are simply pessimistic and nihilistic.
What happens when XR protesters, including Rev. Sue the Anglican priest, glue themselves to commuter trains to press their point about BUSINESS AS USUAL = DEATH? Well, the people who actually have to get to work in the morning take great exception. Even those with deep sympathy for environmental issues are outraged by this arrogant, XR eco-preening.
Set against this bleak outlook is a resurgent conservation ethic on the political right.
Attitudes are shifting toward a more positive engagement on the political Right, with organizations like ConservAmerica and the American Conservation Coalition. This past summer, a group of GOP senators and congressmen formed the Roosevelt Conservation Caucusto restore the party’s credibility on environmental and conservation issues (and to counter the Green New Deal).
While public opinion sentiments on climate change are most pitched on the Left, younger GOP voters are joining them. Talk to conservatives who are active in environmental work, and they will often say things like, “Who doesn’t believe climate change is real?” This despite a healthy skepticism of a debate that is utterly polarized. In their 2015 article “Conservatives and Climate Change, ”Jim Manzi and Peter Wehner said it was not enough to stake out a position of neutrality on climate science.
“Scientific ignorance is not an excuse for refusing to stake out a position,” they wrote. “Politicians rely on engineers to help them figure out which bridges are worth building, on physicists to suggest which defense projects are most feasible, and on biologists to better understand the threat of Ebola or Swine Flu. There is no reason why climate change should be different.”
Why not embrace policies and practices that focus on climate mitigation and adaption, and concrete and practical actions at the ground level that have the potential to make things better? It’s a bet on the future, where there is no room for fatalism or despair.
The philosopher Roger Scruton, who passed away on Jan. 12, described a way forward in his 2012 book How to Think Seriously About the Planet: The Case for Environmental Conservatism. Any environmental movement must be rooted in individual or civic action:
“Environmental problems must be addressed by all of us in our everyday circumstances, and should not be confiscated by the state,” he writes. “Their solution is possible only if people are motivated to confront them, and the task of government is to create those conditions in which the right kind of motive can emerge and solidify.”
To describe these grassroots motives, Scruton coined the word oikophilia (pronounced ECO-philia), or “the love and feeling for home.” The state, he writes, should “make room” for these ground-up efforts, although Scruton’s careful not to demonize every government conservation program. He’s for exploring “the ways in which rational beings can reach co-operative solutions to problems that cannot be addressed either by the individual or the centralized state.”
Scruton defends “initiatives against global schemes, civil association against political activism, and small-scale institutions of friendship against large-scale and purpose-driven campaigns.” On climate change, Scruton describes its appeal partly due to the ability to “internationalize” the problem and present a “calamity so great” that nothing in the way of everyday solutions will do. “The only feasible response to the threat of global warming is to devote our resources to how we might produce energy cheaply and renewably, and then making those discoveries available around the world.”
Read the whole thing at “Beyond the apocalypse: Getting serious about climate and conservation” in Religion & Liberty.
Photo: Extinction Rebellion protest march. Leon Wang / Shutterstock.com. (Editorial use only).